
A Resource Center for HCPs who want to learn more about AZO® products
Information for You and Your Patients
Professional Resources
PACRAN® Abstracts
IN VIVO HUMAN STUDIES EMPLOYING PACRAN®:
Sengupta, K., et al. A randomized, double blind, controlled, dose dependent clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of a proanthocyanidin standardized whole cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) powder on the infections of the urinary tract. Current Bioactive Compounds, 2011; 7:39-46
Sengupta and colleagues conducted a 90 day clinical study to determine the effect of PACran® on bacteriuria and pyuria in women ages 18-40 years old. The data show that PACran® helps to support a healthy urinary tract system. Two different doses of PACran® were studied and compared to an untreated group and to baseline. Significant improvement in symptoms was reported by subjects in both treatment groups by the 10 day evaluation. Women in the untreated group reported no improvement in their symptoms. After the 90 day follow up period, there was a 36% and 65% reduction of urinary E. coli infection reported in the low and high dose groups respectively as compared to baseline. Change in the presence of E.coli at 90 days in the untreated group was not significant when compared to baseline. Both PACran® doses showed significant reduction in urinary E. coli.
Vostalova, J., et al., Are High Proanthocyanidins Key to Cranberry Efficacy in the Prevention of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection?, Phytotherapy Research, 2015; 29: 1559-1567
EX VIVO STUDIES EMPLOYING PACRAN®:
Howell, A., Assessment of bacterial anti-adhesion activity of Pacran® in human urine against P-type uropathogenic Escherichia coli. A randomized, placebo-controlled, ex vivo, double-blind, crossover trial. Rutgers University, 2013
A randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled crossover trial determined the ex vivo anti-adhesion activity toward uropathogenic P-type bacteria in human urine following consumption of either one PACran® capsule or a placebo capsule. The interventions were bracketed by a 7‐day wash‐out period. Anti-adhesive activity was measured over a 60 hour time frame. PACran® had higher total anti-adhesion activity than placebo over all time periods and for all participants combined. By time period, anti-adhesion activity of PACran® was significantly higher than placebo from 9 to 36 hours after ingestion. Placebo ingestion resulted in no significant anti-adhesion activity at any time period.
Additional cross-over comparative studies were conducted at Rutgers University to compare ex vivo bacterial anti-adhesion activity of human urine after consumption of commercially available cranberry products. The results show that PACran® is just as effective as Cranberry Juice Cocktail (ACS Annual Meeting) or two distinct proanthocyanidin (PAC)-rich extracts (Howell 2009b, 2009c) at providing anti-adhesion activity.
Howell, A., Bacterial Anti‐adhesion Activity of Human Urine Following 27% Cranberry Juice Cocktail vs. PACran® Capsule Consumption, presented at ACS 2009 Annual Meeting, 2009a
Howell, A., Bacterial Anti‐adhesion Activity of Human Urine: PACran® Capsule vs. TheraCran®* Capsule Consumption, Rutgers University, 2009b.
Howell, A., Bacterial Anti‐adhesion Activity of Human Urine: PACran® Capsule vs. Urell Capsule Consumption, Rutgers University, 2009c
The third comparative crossover study once again included 5 women and 5 men, ages 25-60 years old. In this case, the interventions included Urell and PACran®. Ex vivo urine anti-adhesion activity was scored for all participants over every time period, totaling 42 out of a possible 120 for Urell and 33 out of 120 for PACran®. The overall difference between the products was not statistically significant. The timepoint analysis suggests that Urell® has a more substantial effect for the first 9 hours, but diminishes thereafter. The PACran® activity appears to slowly increase over time and reaches peak activity at about 24 hours. These ex vivo data support the role of whole cranberry matrices in urinary tract health.
By virtue of the role of PACran® in reducing E.coli adhesion and its equivalence in this regard to other cranberry products, PACran® when taken as directed, promotes a healthy urinary tract.
PACRAN® Abstracts
IN VIVO HUMAN STUDIES EMPLOYING GO-LESS®:
Sogabe, H. and Terado, T., Open Clinical Study of Effects of Pumpkin Seed Extract/soybean Germ Extract Mixture-containing Processed Food on Nocturia., Japanese Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Science, 2001; 46(5):727-727
Terado, T., et al., Clinical study of mixed processed foods containing pumpkin seed extract and soybean germ extract on pollikiuria in night in elderly men., Japanese Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2004; 52(4):551-561
To confirm the efficacy of the supplement containing pumpkin seed extract and soybean isoflavones, 45 males over the age of 65 suffering from nighttime urinary frequency (nocturia) were studied. The supplement reduced nocturia and improved sleep satisfaction. The subjects were divided into two groups; those with concurrent use of therapeutic drugs for nocturia (group A) and those without the use of drugs (group B). The study consisted of a one-week pre-trial observation period, followed by 6 weeks of supplement intake. Subjects recorded the number of times they urinated during the day and night, any adverse symptoms as well as their sleep satisfaction. Adverse events were also objectively evaluated through collection of vital signs and laboratory tests. Daytime urination frequency did not significantly change in either group. For those already taking medication for LUTS symptoms, no significant change in nighttime urination frequency was observed either. This may be an example of a ceiling effect where those men in Group A are already at their optimum given their conditions. The frequency of urination at night for those in group B (drug-free) started to decrease within the first week of taking the supplement and had decreased significantly, by approximately 40%, in this same group by 6 weeks. The supplement was also found to increase sleep satisfaction in the drug-free group but no change was reported by the participants in Group A. Through the use of the participants’ diaries and additional interviews, the investigators summarized each individual’s improvement level. At week 2, two subjects (4.4%) were significantly improved while 28 (62.2%) were improved. Eight men were significantly improved at week 6 while 31 (68.9%) were improved. With respect to adverse events that could possibly be related to the supplement, two participants reported abdominal distension and one presented with itchiness. All three participants were in Group A; those concurrently using therapeutic drugs for pollikiuria. Use of the supplement containing pumpkin seed extract and soybean extract helped to decrease urination frequency at night and improved sleep for the majority of men in this study; mostly for men who were not using other medications for the condition.
Shim, Bongseok, et al., A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial of a product containing pumpkin seed extract and soy germ extract to improve overactive bladder-related voiding dysfunction and quality of life, Journal of Functional Foods, 2014; 8:111-117
Following the success of these earlier studies, a placebo-controlled study of Korean women with overactive bladder syndrome was performed by scientists which was further confirmed the functionality an ingredient blend containing pumpkin seed extract and soybean isoflavones, trademarked GoLess®, for bladder health. The first time point in this study, week 4, confirmed the effect of this current blend of ingredients on urination and frequency of urgency as compared to baseline. Statistically significant improvement in the average frequency of urination (27%) and the average frequency of urgency (31%) was observed at week 12 as compared to baseline. Also at 12 weeks, the average frequency of daytime and nighttime urination was significantly reduced, 27% and 31% respectively, as compared to placebo. Quality of life improved in the treatment group by 22%. A high satisfaction level was reported by treated patients; 90.5% rated the supplement as helpful or very helpful as compared to placebo at 56.1%. In the treatment group, 95.2% expressed interest in continuation of therapy versus 46.3% in the placebo group. No adverse effects were noted. Urgency is a very distressing symptom of overactive bladder syndrome and as such relief of urgency is a key feature of the improvement of LUTS such as those involved in overactive bladder syndrome. The combination of the pumpkin seed extract and soybean germ extract demonstrated safe and fundamental assistance to women with lower urinary tract symptoms such as those associated with overactive bladder syndrome.
This dietary supplement, a mixture of pumpkin seed extract and soybean isoflavones, minimizes urinary incontinence, urination urgency and visits to the bathroom and in so doing helps manage the anxiety associated with finding bathroom facilities in a timely manner. By virtue of these findings, it has been demonstrated that the mixture helps to address the emotional and social consequences of LUTS with fewer adverse effects than many other effective interventions. Given that even after years of supplementing with pumpkin seed extract and soy isoflavones, no serious adverse effects have been reported, the consumer assumes minimal risk and stands to benefit a great deal.
Synetrim® CQ Abstracts
IN VIVO HUMAN STUDIES EMPLOYING CQR-300®:
Oben, J.E., et al., The use of Cissus quadrangularis/Irvingia gabonensis combination in the management of weight loss: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Lipids in Health and Disease, 2008, oi:10.1186/1476-511X-7-12
Reduction in body weight, body fat and waist circumference was observed, with no adverse events, in a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study involving 72 overweight and obese men and women. One of three arms, in which volunteers were administered 300mg/day (150mg twice daily) of CQR-300® for ten weeks, lost 6.7% (p<0.05) more weight than those in the placebo arm; all without dietary restrictions. Body fat was reduced by 14.6% (p<0.05) and waist circumference declined an average of 8.6% (p<0.001) in the CQR-300® group. Participants in the CQR-300® cohort also saw a 26.7% (p<0.05) decrease in total cholesterol and LDL- cholesterol decreased 20.16% (p<0.001) while those taking the placebo saw no statistically significant improvement. Overall the CQR-300® group showed significant improvement in all outcomes compared to the placebo group. CQR-300® formulation may be a useful tool for weight management and metabolic syndrome.
Oben, J.E., et al., The effect of Cissus quadrangularis (CQR-300®) and a Cissus formulation (CORE) on obesity and obesity-induced oxidative stress. Lipids in Health and Disease, 2007, doi:10.1186/1476-511X-6-4
Reduction in body weight, body fat and waist circumference was observed, with no adverse events, in a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study involving 72 overweight and obese men and women. One of three arms, in which volunteers were administered 300mg/day (150mg twice daily) of CQR-300® for ten weeks, lost 6.7% (p<0.05) more weight than those in the placebo arm; all without dietary restrictions. Body fat was reduced by 14.6% (p<0.05) and waist circumference declined an average of 8.6% (p<0.001) in the CQR-300® group. Participants in the CQR-300® cohort also saw a 26.7% (p<0.05) decrease in total cholesterol and LDL- cholesterol decreased 20.16% (p<0.001) while those taking the placebo saw no statistically significant improvement. Overall the CQR-300® group showed significant improvement in all outcomes compared to the placebo group. CQR-300® formulation may be a useful tool for weight management and metabolic syndrome.
Kuate, D., et al., The Use of Cissus quadrangularis (CQR-300®) in the Management of Components of Metabolic Syndrome in Overweight and Obese Participants. Natural product communications, 2015; 1281-1286
A single dose randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study involving 60 healthy participants (31 women and 28 men) administered 300mg CQR-300® (150mg/capsule) or placebo before the first meal of the day, was conducted. Similar to the earlier studies on 150mg CQR-300® dose twice a day, at eight weeks, both overweight and obese participants showed significant reductions in body weight (8.4% and 11.3% respectively), BMI (8.4% and 11.3% respectively) and percent body fat (32% and 26%, respectively) (p<0.05) when taking a single dose of CQR-300®. The waist circumference of the CQR-300® group declined (11% and 13.1% respectively). Hip circumference also declined in both the overweight (8.4%) and obese (13.1%) participants in response to CQR-300®. Additionally, in response to this once a day dose of 300mg CQR-300®, total cholesterol decreased (31% in the overweight and 10% in the obese men and women). Triglycerides were also reduced by 28% in the overweight and 12% in the obese individuals. Serotonin levels rose in the verum cohort; 115% in the overweight and 34 % in the obese. CQR-300®) administered at 300 mg once daily was effective in reducing weight, as well as characteristics associated with metabolic syndrome, as well as serotonin levels, in obese and overweight women and men. This new information confirms the benefits to blood chemistry, body weight and body composition, further substantiating the use of CQR-300® for support of metabolic health and well-being.
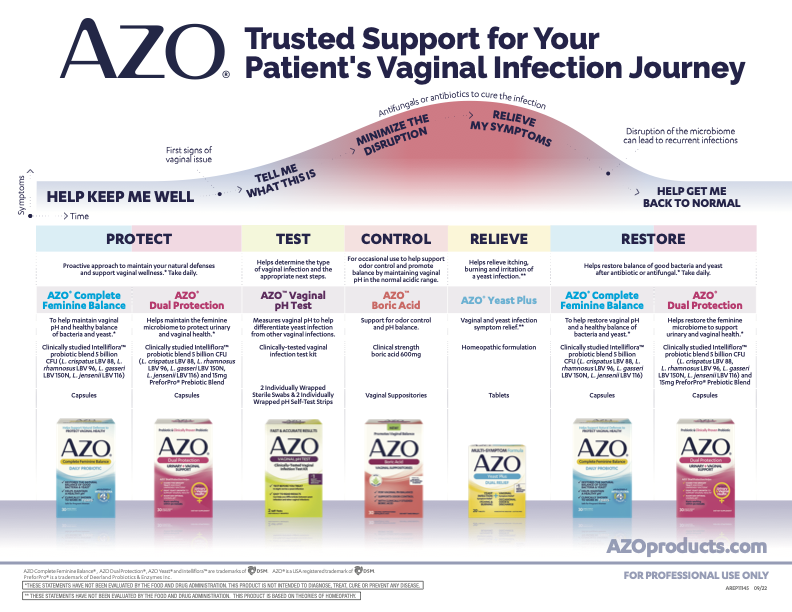
Patient Teaching Tools


SIGN UP
Join our AZO Healthcare Professional Network

RESOURCES
Visit AZO Professional Resources for information and teaching tools
